Επεμβάσεις Στήθους
Αυξητική στήθους, Μείωση στήθους, Ανόρθωση στήθους, Θεραπεία γυναικομαστίας.
Αυξητική Στήθους
 Ό,τι χρειάζεται να γνωρίζετε για την αυξητική στήθους:Η αυξητική στήθους είναι από τις πιο συχνές επεμβάσεις της πλαστικής χειρουργικής στην Κύπρο. Ο πιο σημαντικός λόγος για τον οποίο μια γυναίκα επιθυμεί την αυξητική μαστού είναι ο μικρός μαστός (ανεπαρκής όγκος στήθους) ή αλλιώς υποπλασία μαστού. Λόγω της μεγάλης σημασίας που έχει το στήθος για την ψυχολογίας μίας γυναίκας, γυναίκες με μικρό στήθος μπορεί να έχουν αμφιβολίες για τη θηλυκότητα τους, οδηγώντας τις κάποιες φορές σε έλλειψη αυτοπεποίθησης και αυτοεκτίμησης που μπορεί να αποτελέσει μέχρι και εμπόδιο στην ερωτική τους ζωή.Είναι εντυπωσιακό πως αλλάζει μετά την πλαστική στήθους η όλη συμπεριφορά ...
Ό,τι χρειάζεται να γνωρίζετε για την αυξητική στήθους:Η αυξητική στήθους είναι από τις πιο συχνές επεμβάσεις της πλαστικής χειρουργικής στην Κύπρο. Ο πιο σημαντικός λόγος για τον οποίο μια γυναίκα επιθυμεί την αυξητική μαστού είναι ο μικρός μαστός (ανεπαρκής όγκος στήθους) ή αλλιώς υποπλασία μαστού. Λόγω της μεγάλης σημασίας που έχει το στήθος για την ψυχολογίας μίας γυναίκας, γυναίκες με μικρό στήθος μπορεί να έχουν αμφιβολίες για τη θηλυκότητα τους, οδηγώντας τις κάποιες φορές σε έλλειψη αυτοπεποίθησης και αυτοεκτίμησης που μπορεί να αποτελέσει μέχρι και εμπόδιο στην ερωτική τους ζωή.Είναι εντυπωσιακό πως αλλάζει μετά την πλαστική στήθους η όλη συμπεριφορά ...Ανόρθωση στήθους
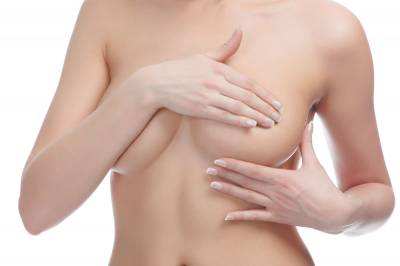
 Το στήθος με την επίδραση των αυξομειώσεων βάρους, την επίδραση της εγκυμοσύνης και της βαρύτητας υφίσταται μεταβολές τόσο στο σχήμα όσο και το μέγεθος. Χάνει την ελαστικότητα του με συνέπεια να χάνει το σχήμα του αλλά και πολλές φορές τον όγκο του και να εμφανίζει αυτό που λέμε πτώση του στήθους. Ο μικρός σε μέγεθος μαστός όταν χάσει τον όγκο του αδειάζει κυρίως και παράλληλα χαλαρώνει, ενώ ο μεγαλύτερος σε όγκο μαστός εμφανίζει την χαρακτηριστική πτώση του στήθους. Το πεσμένο στήθος δημιουργεί έντονο ψυχολογικό πρόβλημα στην γυναίκα μια και δεν μπορεί να αναδείξει το ντεκολτέ και φαίνεται από τα ρούχα ...
Το στήθος με την επίδραση των αυξομειώσεων βάρους, την επίδραση της εγκυμοσύνης και της βαρύτητας υφίσταται μεταβολές τόσο στο σχήμα όσο και το μέγεθος. Χάνει την ελαστικότητα του με συνέπεια να χάνει το σχήμα του αλλά και πολλές φορές τον όγκο του και να εμφανίζει αυτό που λέμε πτώση του στήθους. Ο μικρός σε μέγεθος μαστός όταν χάσει τον όγκο του αδειάζει κυρίως και παράλληλα χαλαρώνει, ενώ ο μεγαλύτερος σε όγκο μαστός εμφανίζει την χαρακτηριστική πτώση του στήθους. Το πεσμένο στήθος δημιουργεί έντονο ψυχολογικό πρόβλημα στην γυναίκα μια και δεν μπορεί να αναδείξει το ντεκολτέ και φαίνεται από τα ρούχα ...Μείωση Στήθους
 Μειωτική Στήθους | Μείωση στήθουςΗ μεγαλομαστία όπως αλλιώς λέγεται αρχίζει από την εφηβεία και συνήθως παραμένει και μετά την εμμηνόπαυση.Φαίνεται, ότι ένας συνδυασμός ορμονών όπως είναι τα οιστρόγονα, η προγεστερόνη, η προλακτίνη και η ινσουλίνη, παίζουν καθοριστικό ρόλο. Αυτή η αύξηση του στήθους στη γυναίκα αφορά αφ’ ενός μεν τον αδένα και αφ’ ετέρου το λίπος που βρίσκεται ανάμεσα και γύρω απ’ αυτόν.Μπορούμε να χειρουργήσουμε μια γυναίκα αμέσως μόλις τελειώσει το λύκειο (18-ετών) έως και μετά την εμμηνόπαυση . Η ηλικία των 18 ετών θεωρείται το ελάχιστο όριο για μια νεαρή κοπέλα μιας και τότε διαμορφώνεται το στήθος. Οι περισσότερες ...
Μειωτική Στήθους | Μείωση στήθουςΗ μεγαλομαστία όπως αλλιώς λέγεται αρχίζει από την εφηβεία και συνήθως παραμένει και μετά την εμμηνόπαυση.Φαίνεται, ότι ένας συνδυασμός ορμονών όπως είναι τα οιστρόγονα, η προγεστερόνη, η προλακτίνη και η ινσουλίνη, παίζουν καθοριστικό ρόλο. Αυτή η αύξηση του στήθους στη γυναίκα αφορά αφ’ ενός μεν τον αδένα και αφ’ ετέρου το λίπος που βρίσκεται ανάμεσα και γύρω απ’ αυτόν.Μπορούμε να χειρουργήσουμε μια γυναίκα αμέσως μόλις τελειώσει το λύκειο (18-ετών) έως και μετά την εμμηνόπαυση . Η ηλικία των 18 ετών θεωρείται το ελάχιστο όριο για μια νεαρή κοπέλα μιας και τότε διαμορφώνεται το στήθος. Οι περισσότερες ...Γυναικομαστία
 Τι είναι η γυναικομαστία;Η γυναικομαστία είναι η ανάπτυξη στους άνδρες μεγάλου στήθους. Αυτό μπορεί να τους προκαλέσει προβλήματα σχετικά με την εμφάνισή τους, επηρεάζοντας παράλληλα και την ανδρική αυτοπεποίθησή τους. Πολλοί ασθενείς αποφεύγουν να εκθέτουν το στήθος τους στην παραλία, στο γυμναστήριο κ.λ.π. Επίσης, περιορίζει τις επιλογές τους στο ντύσιμο, αποφεύγοντας ρούχα που είναι πολύ εφαρμοστά. Ιδιαίτερα στην Κύπρο, μπορεί να προκαλέσει αρκετά ψυχολογικά προβλήματα κατά την διάρκεια της στρατιωτικής θητείας του έφηβου.Αιτιολογία:Η πιο συχνή μορφή είναι η λεγόμενη εφηβική γυναικομαστία. Εμφανίζεται σε ποσοστό 40% των εφήβων, σε ηλικίες μεταξύ 13 και 17 ετών και είναι αμφοτερόπλευρη (και τα δυο ...
Τι είναι η γυναικομαστία;Η γυναικομαστία είναι η ανάπτυξη στους άνδρες μεγάλου στήθους. Αυτό μπορεί να τους προκαλέσει προβλήματα σχετικά με την εμφάνισή τους, επηρεάζοντας παράλληλα και την ανδρική αυτοπεποίθησή τους. Πολλοί ασθενείς αποφεύγουν να εκθέτουν το στήθος τους στην παραλία, στο γυμναστήριο κ.λ.π. Επίσης, περιορίζει τις επιλογές τους στο ντύσιμο, αποφεύγοντας ρούχα που είναι πολύ εφαρμοστά. Ιδιαίτερα στην Κύπρο, μπορεί να προκαλέσει αρκετά ψυχολογικά προβλήματα κατά την διάρκεια της στρατιωτικής θητείας του έφηβου.Αιτιολογία:Η πιο συχνή μορφή είναι η λεγόμενη εφηβική γυναικομαστία. Εμφανίζεται σε ποσοστό 40% των εφήβων, σε ηλικίες μεταξύ 13 και 17 ετών και είναι αμφοτερόπλευρη (και τα δυο ...Εσολκή θηλής
Όταν έχουμε μία θηλή, η οποία αντί να προεξέχει προς τα έξω εισέρχεται προς τα μέσα, τότε μιλάμε για εσολκή θηλής. Μπορεί να οφείλεται στο ότι οι γαλακτοφόροι πόροι, δηλαδή τα σωληνάκια που μεταφέρουν το γάλα από τον αδένα προς τη θηλή, είναι κοντύτεροι από το συνηθισμένο. Σε άλλες περιπτώσεις η εσολκή της θηλής μπορεί να οφείλεται σε χειρουργικές επεμβάσεις που προηγήθηκαν στην περιοχή, σε μόλυνση ή γενικότερα σε κάποια φλεγμονή των γαλακτοφόρων πόρων.Κάποιες λίγες φορές μπορεί να οφείλεται και σε καρκίνο του μαστού. Γενικά, θεωρείται ένα αισθητικό πρόβλημα, όμως συνήθως δημιουργεί κάποια λειτουργικά προβλήματα, όπως αδυναμία θηλασμού. Εσολκή θηλής ...